Contents
Contents
- What Are the Material Options for Intake Manifolds?
- Characteristics of Aluminum Intake Manifolds
- Characteristics of Cast Iron Intake Manifolds
- Aluminum Intake Manifold vs Cast Iron Intake Manifold: A Complete Comparison Table
- Application Scenarios: Which Intake Manifold is Right for You?
- Maintenance Tips for Aluminum Intake Manifolds
- Conclusion
The intake manifold plays a crucial role in engine performance. Like the engine's breathing system, it precisely distributes air to each cylinder. If you're planning to modify your engine to improve performance, the intake manifold material is a key consideration.
One of the most frequently discussed topics is: aluminum intake manifold vs. cast iron intake manifold – which should you choose? Below, we'll quickly outline their differences to help you determine which is more suitable for your engine platform and modification goals.

What Are the Material Options for Intake Manifolds?
Common Intake Manifold Materials
- Aluminum/Aluminum Alloy: Most commonly used in high-performance modifications.
- Cast Iron: Older engines, heavy-duty applications.
- Plastics/Composite Materials: Widely used in modern factory vehicles.
- Carbon Fiber: High-end racing applications.
Each material has different properties that affect performance, cost, and durability. Please refer to the table below.
Key Properties of Intake Manifold Materials
| Property | Aluminum | Cast Iron | Plastic/Composite | Carbon Fiber |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | Very light | Very heavy | Light | Extremely light |
| Heat Resistance | High | Very high | Moderate | High |
| Heat Dissipation | Excellent | Poor | Good | Excellent |
| Cost | Moderate | Low | Low | High |
| Modification Potential | High | Low | Low | Medium |
| Strength | Strong | Very strong | Moderate | Strong but brittle |
Characteristics of Aluminum Intake Manifolds
Aluminum intake manifolds are the choice of most aftermarket enthusiasts. Let's take a look at its advantages and disadvantages.
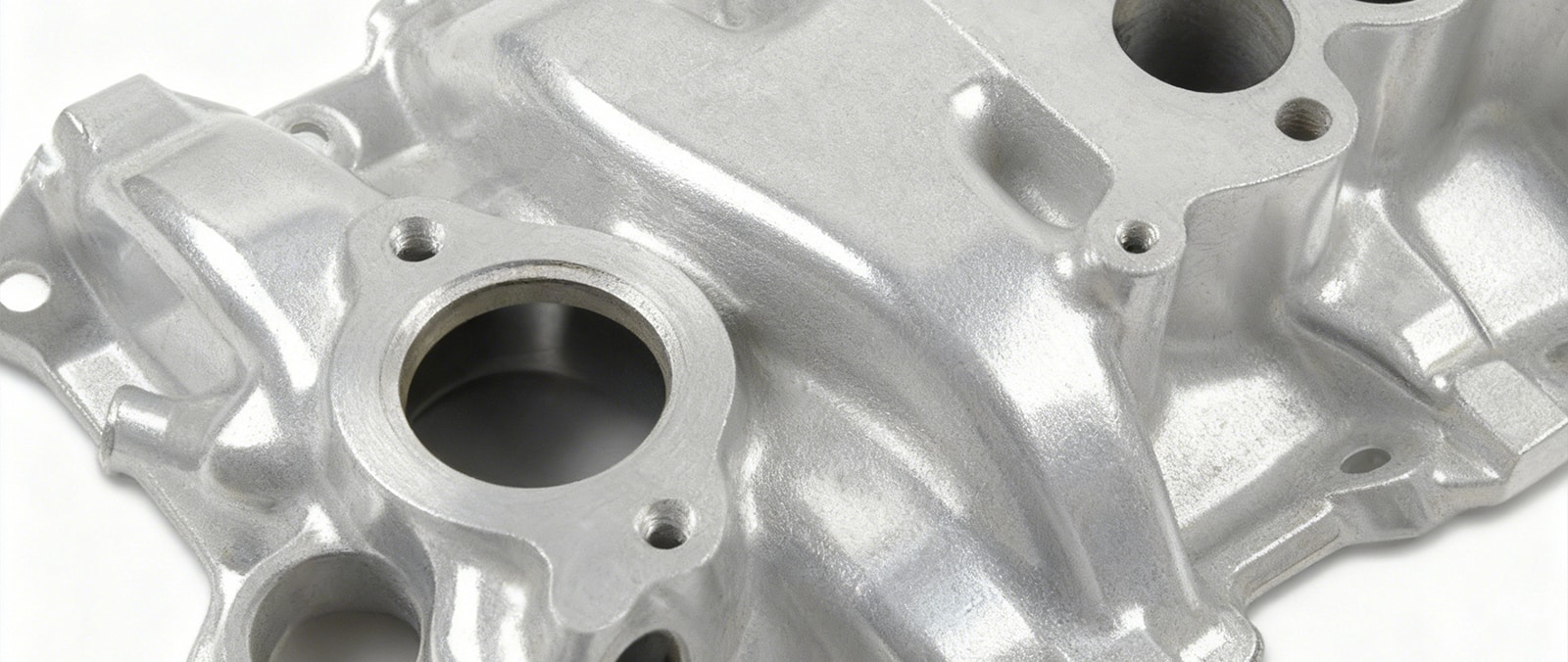

Advantages
- Lightweight: Typical aluminum manifolds are 30-50% lighter than cast iron manifolds of the same size.
- Superior Heat Dissipation: Aluminum has excellent heat dissipation properties, reducing intake air temperature.
- Easy to Retrofit and Customize: Aluminum is easy to weld, allowing for customized intake pipe designs.
- High Heat Resistance and High Boost Pressure Tolerance: Aluminum can withstand higher intake air temperatures and higher boost pressures.
- Value for Money: Aluminum intake manifolds are moderately priced, typically more affordable than carbon fiber manifolds and comparable in price to high-quality cast iron manifolds.
- Corrosion Protection Required: Aluminum is susceptible to electrochemical corrosion (especially in contact with steel bolts or other metals).
- Cost is generally higher than plastic/composite materials.
- In the extreme high-temperature, high-pressure conditions of racing, aluminum intake manifolds may not be as rigid as thick-walled cast iron.
Disadvantages
Characteristics of Cast Iron Intake Manifolds
Cast iron was once the standard material for intake manifolds and still holds a place in certain applications. Let's weigh the advantages and disadvantages of cast iron:
Advantages
- Cast iron is extremely tough and can withstand decades of use, vibration, and harsh environments.
- Resistant to thermal stress cracking.
- Suitable for heavy-duty engines and older trucks.
- Remains stable at extremely high temperatures.
- Basic cast iron manifolds are generally cheaper than aluminum manifolds.
Disadvantages
- Excessive weight: Negatively impacts acceleration performance and fuel economy.
- Poor heat dissipation: Increases intake air temperature.
- Cast iron is relatively brittle, making it difficult to modify or machine.
- Cast iron is prone to rusting.
Aluminum Intake Manifold vs Cast Iron Intake Manifold: A Complete Comparison Table
To more clearly illustrate the differences between the two, the following is a detailed comparison table of cast iron and aluminum intake manifolds:
| Feature | Aluminum Intake Manifold | Cast Iron Intake Manifold |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Very light | Very heavy |
| Heat Dissipation | Excellent | Poor |
| Durability | Strong; needs corrosion protection | Extremely durable |
| Modification | Easy to tune, port, weld, machine | Difficult to customize |
| Boost Compatibility | Highly suitable | Strong but heavy and inefficient |
| Fuel Economy Impact | Easy to tune, port, weld, machine | Difficult to customize |
| Cost | Moderate | Low |
| Performance Gains | Noticeable improvements | Minimal benefits |
Conclusion:
Aluminum intake manifolds demonstrate superior performance, flexibility, and efficiency in virtually all modern automotive environments. This direct comparison reveals why aluminum has become the preferred choice for most modern applications.
Application Scenarios: Which Intake Manifold is Right for You?
The best intake manifold choice depends on your vehicle, intended use, and goals. Here's a tailored guide:
1. Daily Driving/Commuting – Aluminum Intake Manifold

For daily drivers on a budget, choosing an aluminum intake manifold is a cost-effective option. It's superior to cast iron or plastic in everyday use, yet it's not expensive.
Aluminum products are also superior to cast iron or plastic in everyday use.
2. High Performance/Turbocharging/Modification/Racing – Aluminum Intake Manifold/Carbon Fiber
Aluminum intake manifolds are the best choice for these types of vehicles. Their lightweight design, excellent heat dissipation, and modification flexibility are ideal for them. Carbon fiber is also an option - but it's more expensive.
3. Older Vehicles/Heavy Trucks – Cast Iron/Aluminum Intake Manifold
If you're maintaining an older carburetor vehicle or a heavy truck with low performance requirements, a cast iron intake manifold may suffice. However, upgrading to an aluminum manifold can still improve fuel economy without sacrificing durability.
Maintenance Tips for Aluminum Intake Manifolds
While aluminum intake manifolds are durable, proper maintenance can ensure a lifespan of decades. Please follow these tips:
- Cleaning Precautions: Avoid using corrosive chemicals (such as strong degreasers) to prevent damage to the aluminum surface. Always use mild cleaners and soft brushes.
- Inspect Seals and Bolts: Regularly inspect the manifold gaskets, seals, and bolts for wear or loosening.
- Control High Temperatures: Although aluminum has good heat resistance, avoid prolonged idling at extreme temperatures.
- Prevent Corrosion: If your vehicle's coolant comes into contact with the intake manifold, use a coolant compatible with aluminum to avoid galvanic corrosion.
Conclusion
In summary, the comparison between aluminum and cast iron intake manifolds is quite clear. For most modern applications, aluminum intake manifolds strike a better balance between performance, heat dissipation, and ease of modification, making them the preferred upgrade choice.
Quick Decision Guide: If your goal is to improve responsiveness or facilitate future modifications, choose an aluminum intake manifold; if you are maintaining a classic vehicle or heavy-duty platform and do not require modifications, a cast iron intake manifold remains a viable option.