Contents
Contents
- What Does P2003 Mean?
- What Are the Symptoms of Code P2003?
- Top Reasons Why You're Getting a P2003 Code
- How to Diagnose the P2003 Code? (Step-by-Step Guide)
- How to Fix Code P2003 and Restore DPF Efficiency
- Which Vehicles Are Affected by P2003?
- How Much Does It Cost to Fix Code P2003?
- How to Prevent P2003 Code
- Frequently Asked Questions about P2003
- Conclusion
You're driving to the office already late, when suddenly the check engine light (CEL) illuminates and your car goes into limp mode. Luckily, you have a scanner tool in your vehicle, and when you attach it, you see the code P2003 - Diesel Particulate Filter Efficiency Below Threshold.
Is the issue serious? Can you still drive to your workplace like this?
this is something diesel truck owners face quite frequently: the DPF gets clogged, the fuel economy is low, and the engine is not performing as it should. While this might seem like a minor hindrance, if left unchecked, this issue can seriously damage your vehicle.
In this article, we'll explain what P2003 means, its symptoms, causes, and repair costs, as well as tips for avoiding future DPF issues.
- Code P2003 means Diesel Particulate Filter Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 2).
- Causes: Clogged DPF, faulty DPFE sensor, or exhaust leaks.
- Symptoms: Check Engine Light, poor fuel economy, reduced power.
- Fix: Perform forced regeneration or replace faulty components.
- Severity: Moderate to severe. Fix promptly to prevent engine damage.

What Does P2003 Mean?
The error code P2003 stands for " Diesel Particulate Filter Efficiency Below Threshold Bank 2 ".
The Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) isn't working properly in the 'Bank 2' area of the engine. This issue arises when the DPF isn't able to capture soot particles and complete the regeneration process, necessary to 'clean' the exhaust gases.
Some of you may ask: "But what is Bank 2?"
Well, V-type engines have two rows of cylinders, designated as 'Bank 1' and 'Bank 2'. This particular fault code is generated when the Bank 2 side DPF develops a fault.
How Is the Code Triggered?
The ECM calculates DPF efficiency using data from the DPF differential pressure sensor and exhaust gas temperature (EGT) sensors. When it detects a pressure difference that falls outside the acceptable range, it stores P2003 and may limit engine performance to protect the turbo and exhaust system.
✅ Note: P2003 is similar to P2002 (Bank 1), and both are among the most common DPF-related OBD-II codes.
Importance of the DPF
The DPF is part of the system that battles the NOx gases produced by the engine. It turns the harmful gases into simple Nitrogen, Oxygen and Carbon that can then be released through the exhaust system out in the environment.
In other words, it is extremely necessary that this system is working, or your car could fail the emissions test!
What Are the Symptoms of Code P2003?
Check Engine Light (CEL) Illuminates : When the DPF efficiency is below the threshold, the ECM detects the issue and triggers the Check Engine Light (CEL).
Severity: Mild
Reduced Engine Performance : A faulty DPF will restrict the flow of exhaust gases, causing the car to experience slow acceleration or go into limp mode. One user on r/MechanicAdvice reported the same with his diesel Subaru.
Severity: Immediate Attention
Poor Fuel Economy : According to a study, when ash deposits increase, the exhaust back-pressure increases, which worsens fuel consumption and engine power. Another DieselNet study states that DPF clogging leads to a 2-3% worse fuel economy.
Severity: Immediate Attention
Loud Engine Sound: A clogged or underperforming DPF can cause rough idling and increase engine noise.
Severity: Mild
Top Reasons Why You're Getting a P2003 Code
Listed below are things that can cause the DPF to become inefficient:

- Clogged DPF : Excessive carbon buildup in the DPF prevents proper regeneration, triggering the ECM to display the Check Engine Light (CEL).
- Bad DPFE Sensor : A faulty Differential Pressure Feedback EGR (DPFE) sensor sends incorrect readings to the ECM, triggering the error code.
- Upstream or Downstream Leaks : There are leaks in the air intake or the exhaust system, which are affecting the regeneration cycle, causing the DPFE sensor to send inaccurate data to the ECM.
How to Diagnose the P2003 Code? (Step-by-Step Guide)
Here are the tools that you'll need before you set out to diagnose the issue:
Tools You'll Need:
- OBD-II scanner
- Owner manual/workshop manual
- Car jack
Step 1: Scan for Similar Codes
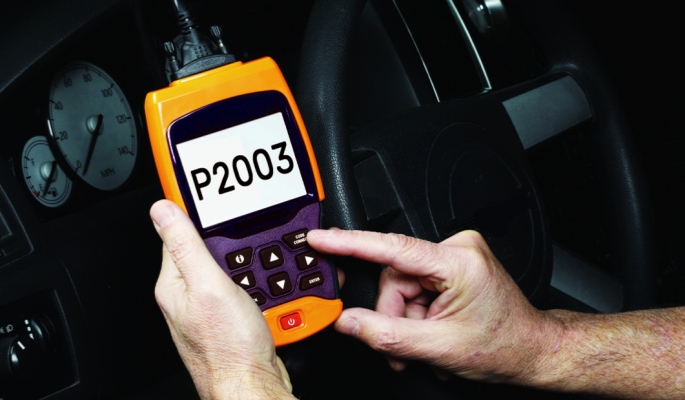

- Use the OBD-II scanner to look for codes related to sensor or regeneration issues.
- If the ECM has registered similar codes in the past, it is best practice to look at the older problem area first, before going further with the repair.
Step 2: Check the DPFE Sensor
- Use the OBD-II scanner to look for codes related to sensor or regeneration issues (check all OBD codes here: https://www.suncentauto.com/obd-ii-codes-list)
- Compare the readings with the workshop manual and see if they are according to the manufacturer's specifications.
Step 3: Check the Exhaust System
- Lift the car using the jack, and inspect the exhaust system for leaks.
- Look closely at the exhaust pipes near the Bank 2 area of the engine, since that's where the fault lies.
- Also, inspect the Bank 2 area from inside the engine bay for damage or leaks.
How to Fix Code P2003 and Restore DPF Efficiency
If your car has a DPF problem, here are some repairs you can do to rectify the issue:
Clear Carbon Deposits
The DPF regeneration cycle is activated by the ECM when it detects soot buildup. During regeneration, the system uses high temperatures to burn off the soot. (Note: Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) is used in the separate Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) system to reduce NOx gases, not directly in the DPF regeneration process).
You can trigger a forced regeneration procedure through an advanced OBD-II scanner, which should help clean the buildup of excessive carbon.
Replace the DPFE Sensor
Check the readings from the sensor against the optimal readings found in the service manual specific to your vehicle. If the data is inaccurate, change the DPFE sensor.
Replace Damaged Components
If the exhaust components or any other parts around the Bank 2 area of the engine are damaged or leaking, replace them for optimal DPF function.
Remove the DPF
You can choose to install an aftermarket DPF delete kit to bypass the filter and avoid fault codes. However, this modification is illegal in many states and may result in non-compliant emissions. Removal kits are for off-road, racing, or track use only. Always consult with local laws and regulations and a certified technician before considering such modifications.
Which Vehicles Are Affected by P2003?
| Make / Model | Years / Engine types most affected | Typical anomaly | Vehicle-specific repair tips |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dodge Ram 1500 | V6 EcoDiesel engines found in 2014-2019 models. | Problems with dispensing Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) due to pump failure or heater failure in winter. | Perform forced regeneration and check the DPFE sensor before changing any components. |
| Ford F-Series Super Duty | Mid-2010 models with Power Stroke diesel engines. | Fuel with high sulfur causes clogging of the DPF. The EGR valve is also known to fail in this vehicle, resulting in soot buildup. | Regularly clean the EGR and perform a forced regeneration to clean the DPF. |
| Chevrolet Silverado/GMC Sierra | Early and mid-2010 Duramax diesel engines. | Intake leaks and sensor malfunctions are common issues in these vehicles. | Check the DPFE sensor for accuracy and inspect the intake for leaks. |
| Mercedes-Benz Sprinter | The P2003 Mercedes fault code appears in the OM642 V6 diesel engine and BlueTEC 2.0L turbo-diesel engine. | The P2003 code appears due to sensor malfunction or driving most of the time in low speeds. | The Mercedes-Benz P2003 fault code can be solved by using correct engine oil, regular maintenance and initiating regen cycle frequently. |
How Much Does It Cost to Fix Code P2003?
Factors such as model, make, year, labor rates, and parts availability can affect prices. Keeping that in mind, here are some repair cost estimates for a code P2003 DPF fault:
| Item | Part / Cost Estimate | DIY or Professional Help |
| Diagnosis (sensor check, OBD scan, DPF inspection) | $150-$300 including labor | It can be done at home, but you should seek professional help. |
| Sensor Replacement | $200-$500 with labor | You can do this one yourself with the right tools. |
| Forced DPF Regeneration | $150-$600 including labor | It can be a DIY project if you have the right tools. |
| DPF Clean (off-vehicle) | $500-$1500 with labor | Better to seek professional help, but it can be done with the proper tools. |
| DPF Replacement | $2500-$6000+ with labor | Better to seek professional help, but it can be done with the proper tools. |
How to Prevent P2003 Code
Here's what you can do to prevent DPF issues from affecting your vehicle:
Regular Highway Driving : Driving at highway speeds for 20 or 30 minutes once every two weeks can help burn off excess soot in the exhaust system and keep the DPF healthy.
Avoid Unnecessary Idling : Limit yourself from idling your vehicle for too long, as it reduces exhaust gas temperatures and promotes carbon buildup.
Change Driving Habits : Try driving at constant speeds, because frequent acceleration and deceleration can promote carbon buildup in the exhaust.
Let the Regeneration Cycle Finish : When your engine is showing signs of regeneration, like higher engine noise, higher idle rpm, or the radiator fan running, do not turn it off. Killing the engine at that time can promote soot buildup.
Use Suncent DPF Delete Kit : One of the ways to prevent a P2003 fault code is by bypassing the Diesel Particulate Filter. If you install a DPF Delete Kit you can essentially rid yourself of DPF-related problems and never get the code again. However, this behavior is illegal in many places, so be sure to check before doing it.
Frequently Asked Questions about P2003
Conclusion
The P2003 fault code is a serious issue that requires immediate attention to prevent engine damage. Fortunately, it can be resolved using methods ranging from forced regeneration to sensor replacement. If you require a permanent, off-road-only solution, consider using a DPF removal kit!