Your car engine is a complex ecosystem where all the parts work in harmony—until one of them breaks down. One of the most misunderstood yet critical parts is the EGR valve. If your vehicle has ever shuddered at a stoplight or consumed fuel unexpectedly, this little device could be the culprit. Let’s demystify the EGR valve and learn what it does, how to spot a problem, and how to keep it running smoothly.

What Is an EGR Valve?
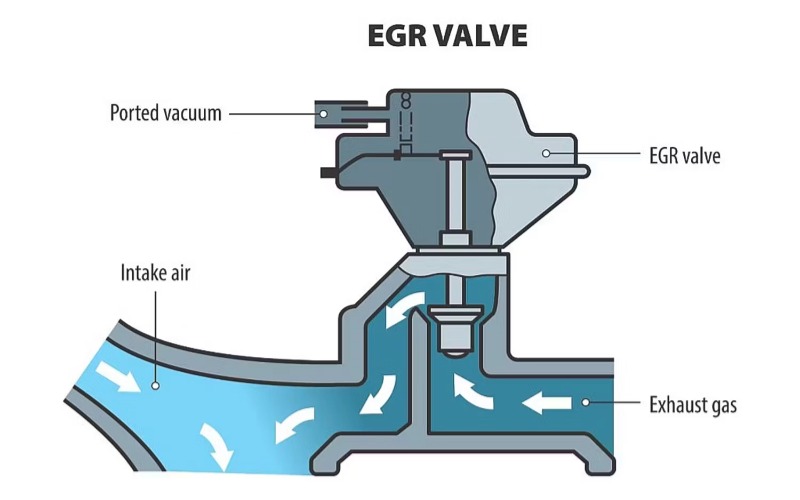
EGR stands for Exhaust Gas Recirculation and it is an important part of the vehicle's engine system. You can think of it as a recovery system for the engine. This system sends a small portion of the exhaust gases produced by a diesel or gasoline engine back into the cylinders. It is designed to reduce harmful NOx emissions, which are the main cause of air pollution.
The EGR system includes the EGR valve, EGR cooler, piping, and connections. The EGR valve is the main component of this system, which is used to control the flow of exhaust gases back into the engine. It is located between the exhaust manifold and the intake manifold and is usually a small metal valve connected to a vacuum hose or wire.
What Does an EGR Valve Do?
We just said that the EGR valve is used to reduce the formation of dangerous nitrogen oxides (NOx). So how does it do this specifically? Let's take a look at how the EGR valve works.
Nearly 80% of the air we breathe is nitrogen. Although nitrogen is harmless in its natural state, it can turn into dangerous nitrogen oxides (NOx) when exposed to extreme heat. And the temperature in the combustion chamber of a car engine is at least 1,370°C. So this is where the EGR valve comes in.
The EGR valve redirects some of the exhaust gas from the exhaust manifold to the intake manifold, where it mixes with fresh air before re-entering the combustion chamber. This lowers both the peak combustion temperature and reduces gas emissions.
This has two major benefits. First, it minimizes the formation of nitrogen oxides, helping your vehicle meet strict emission standards. Second, it reduces control temperatures and extends engine life.
Types of EGR Valves
To meet the ever-changing emission standards, EGR valves have evolved step by step. Let's analyze the four main types of EGR valves and their unique roles.
1. Diesel EGR Valve:
There are two different types of diesel EGR systems: high pressure and low pressure.
1.1 High-pressure EGR system:
The valves are located upstream of the diesel particulate filter (DPF). They divert the exhaust gases before they reach the turbocharger, recirculating them into the intake manifold.
High-pressure systems are common in older diesel engines because they are simpler and more responsive. However, they increase soot accumulation and reduce the efficiency of the turbocharger.
1.2 Low-pressure diesel EGR valve:
The valves are located after the DPF and recirculate the exhaust gases only after they have been filtered. This ensures that soot rarely re-enters, so these gases are cooler and cleaner, reducing engine wear.
However, low-pressure systems require additional components, such as EGR coolers and complex piping.
2. Vacuum-operated EGR valve
For older vehicles (pre-2000), the vacuum-operated EGR valve is more common. It uses engine vacuum pressure to control exhaust gas flow.
3. Electronic EGR valve (ECU-controlled)
Modern petrol and diesel engines all use an electronic EGR valve. It is managed by the engine control unit (ECU) and allows for more precise control of exhaust gas flow.
4. Digital EGR valve
The digital EGR valve is a further development of the electronic EGR valve and is used in newer vehicles (post-2010s). It replaces the analog signal with a full computer control, which is more precise.
Symptoms of a Bad EGR Valve
More significant engine issues can be avoided by promptly recognizing the signs of a malfunctioning EGR valve. The following are the main indicators to look for:
- The Check Engine Light (CEL) was on
- Engine stalling or rough idle
- Low power and poor acceleration
- A rise in gasoline usage
- Explosion or engine knock
- A rise in emissions and the failure of emissions tests
- A strong smell of petrol or exhaust
In addition to the above signs, you can use an OBD-II scanner to scan for diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). Common EGR trouble codes include:
- P1404: Valve Needle/Actuator Error
- P0400: Flow Fault
- P0401: Insufficient EGR Flow
- P0402: Excessive EGR Flow
If any of these codes appear, the EGR valve may be faulty. Thankfully, you can avoid problems caused by a faulty EGR valve by using an EGR delete kit.
Maintaining Your EGR Valve
To guarantee optimum engine performance, fuel economy, and lower emissions, the EGR valve must receive routine maintenance. You can prolong the life of your EGR valve and prevent expensive repairs by adhering to these maintenance guidelines:
- 1. Clean the EGR valve regularly
- 2. Inspect and clean the EGR passages
- 3. Use high-quality fuel and additives
- 4. Drive at highway speeds regularly
- 5. Inspect vacuum hoses and electrical connections
- 6. Follow the manufacturer's maintenance schedule
- 7. Replace the EGR valve when necessary
FAQs About EGR Valves
If you're having issues with your vehicle's EGR valve or just want to learn more about how it works, here are answers to some of the most common questions.
1. What is an EGR valve?
The EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) valve is a component of the internal combustion engine that helps reduce nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions. By recirculating part of the exhaust gas back into the intake manifold, it reduces combustion temperatures and improves efficiency.
2. How does an EGR valve work?
The EGR valve works by recirculating a portion of the exhaust gas back into the combustion chamber. It reduces low peak combustion temperatures and reduces the formation of nitrogen oxides.
3. Can a vehicle with a faulty EGR valve continue to be driven?
While you can drive a vehicle with a faulty EGR valve, doing so is not recommended. It may result in reduced engine performance, increased emissions, and possible long-term damage due to excessive combustion temperatures. It is best to have the problem inspected and repaired as soon as possible.
4. How often should I clean the EGR valve?
The cleaning interval depends on driving conditions and fuel quality. In general:
Vehicles driven in city traffic or short distances should have their EGR valves inspected and cleaned every 30,000 to 50,000 miles.
Vehicles that are driven on the highway generally have fewer carbon deposits, but the system should still be checked regularly.
If your check engine light displays a code related to EGR, you may need to clean it sooner rather than later.
Conclusion
Now you know what an EGR valve is and what it does. The EGR valve is a small but vital component in modern vehicles that is designed to reduce harmful nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions. Among other things, it balances engine performance and improves fuel efficiency. We recommend being proactive about your vehicle's health and maintaining your EGR valve regularly.
















































